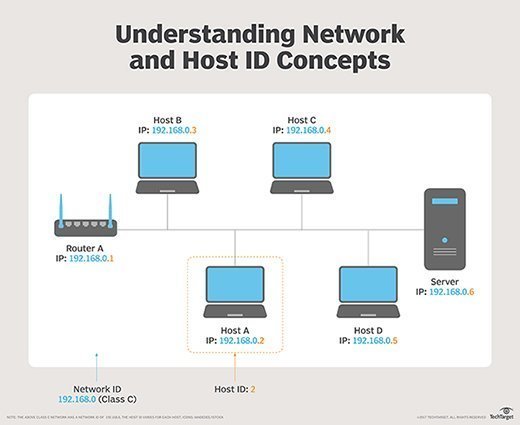
On a TCP/IP network, each host has a host number that, together with a network identity, forms its own unique IP address. In the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model, protocols in the transport layer, also known as Layer 4, are responsible for communication between hosts. Hosts use various protocols to communicate, including transmission control protocol (TCP) and User Datagram Protocol (UDP).
Types of IT hosts
The term host is used in several other areas within information technology (IT), carrying a slightly different meaning depending on the context.
Web host. For companies or individuals with a website, a host is a web server that stores and transmits the data for one or more websites. Host can also refer to the service provider that leases this infrastructure, which is known as hosting.
Cloud host. A cloud host is based on cloud computing technologies that allow a number of servers to act as one system in which website performance can be guaranteed by multiple machines. It often includes a network of servers pulling from different data centers in different locations. Cloud hosts operate as a service that allows clients to buy as much of the service as they need. Cloud hosting is an alternative to hosting a website on a single server. Cloud hosting can be considered both infrastructure as a service (IaaS) and platform as a service (PaaS). Using a public cloud model, a public network transmits data that is physically stored on virtual servers and uses public networks to transmit the data that is physically stored on shared servers that make up the cloud resource.
Virtual host. The term virtual host has two uses. One refers to the technology used to run multiple domains or applications on a single physical server, and the second refers to companies that sell virtual infrastructure services.
Remote host. In this context, a remote host is in a different physical location than the user accessed using a private network or the internet, which provides users with remote access. Examples include servers that can be logged into remotely or a host computer for a remote desktop.
Host virtual machine. This refers to the hardware — that is, the physical server — that provides the computing resources to support virtual machines (also known as server virtualization).
Mainframe computer environments. In this context, a mainframe computer can be the host provider of services for the workstations attached to it. This does not mean that the host only has “servers” and that the workstations only have “clients.” The server-client relationship is a programming model independent of this contextual usage of “host.”
Hostname. A hostname is a plaintext name identifying a host in a given domain. On a local area network (LAN), a server’s hostname might be a nickname like mailserver1. On the internet, a hostname makes up part of a web address and has three parts: the subdomain, domain name and top-level domain. For example, the hostname whatis.techtarget.comconsists of the subdomain whatis, the domain techtarget and the top-level domain .com.
In other contexts, a host can also be a device or program that provides services to some smaller or less-capable device or program.