Risk Map (risk heat map) Definition
A risk map, also known as a risk heat map, is a data visualization tool for communicating specific risks an organization faces. A risk map helps companies identify and prioritize the risks associated with their business.
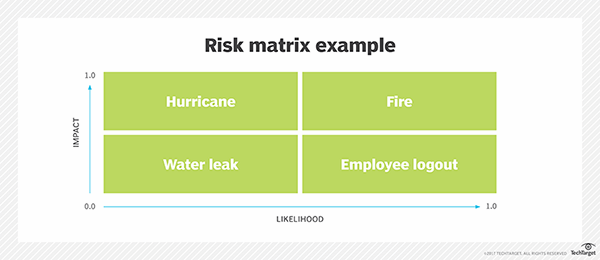
The goal of a risk map is to improve an organization’s understanding of its risk profile and appetite, clarify thinking on the nature and impact of risks, and improve the organization’s risk assessment model. In the enterprise, a risk map is often presented as a two-dimensional matrix. For example, the likelihood a risk will occur may be plotted on the x-axis, while the impact of the same risk is plotted on the y-axis.
A risk map is considered a critical component of enterprise risk management because it helps identify risks that need more attention. Identified risks that fall in the high-frequency and high-severity section can then be made a priority by organizations. If the organization is dispersed geographically and certain risks are associated with certain geographical areas, risks might be illustrated with a heat map, using color to illustrate the levels of risk to which individual branch offices are exposed.
How to create a risk map
Identification of inherent risks is the first step in creating a risk map. Risks can be broadly categorized into strategic risk, compliance risk, operational risk, financial risk and reputational risk, but organizations should aim to chart their own lists by taking into consideration specific factors that might affect them financially. Once the risks have been identified, it is necessary to understand what kind of internal or external events are driving the risks.
The next step in risk mapping is evaluating the risks: estimating the frequency, the potential impact and possible control processes to offset the risks. The risks should then be prioritized. The most impactful risks can be managed by applying control processes to help lessen their potential occurrence.
As threats evolve and vulnerabilities change, a risk map must be re-evaluated periodically. Organizations also must review their risk maps regularly to ensure key risks are being managed effectively.
Why it’s important to create a risk map
A risk map offers a visualized, comprehensive view of the likelihood and impact of an organization’s risks. This helps the organization improve risk management and risk governance by prioritizing risk management efforts. This risk prioritization enables them to focus time and money on the most potentially damaging risks identified in a heat map chart.
A risk map also facilitates interdepartmental dialogues about an organization’s inherent risks and promotes communication about risks throughout the organization. It helps organizations visualize risks in relation to each other, and it guides the development of a control assessment of how to deal with the risks and the consequence of those risks.
The map can help the company visualize how risks in one part of the organization can affect operations of another business unit within the organization.
A risk map also adds precision to an organization’s risk assessment strategy and identifies gaps in an organization’s risk management processes.