Open Database Connectivity (ODBC)
The main proponent and supplier of ODBC programming support is Microsoft, but ODBC is based on and closely aligned with The Open Group standard Structured Query Language (SQL) Call-Level Interface (CLI). The Open Group is sponsored by many major vendors, including Oracle, IBM and Hewlett Packard Enterprise, and this consortium develops and manufactures The Open Group Architecture Framework (TOGAF). In addition to CLI specifications from The Open Group, ODBC also aligns with the ISO/IEC for database APIs.
How ODBC works
ODBC consists of four components, working together to enable functions. ODBC allows programs to use SQL requests that access databases without knowing the proprietary interfaces to the databases. ODBC handles the SQL request and converts it into a request each database system understands.
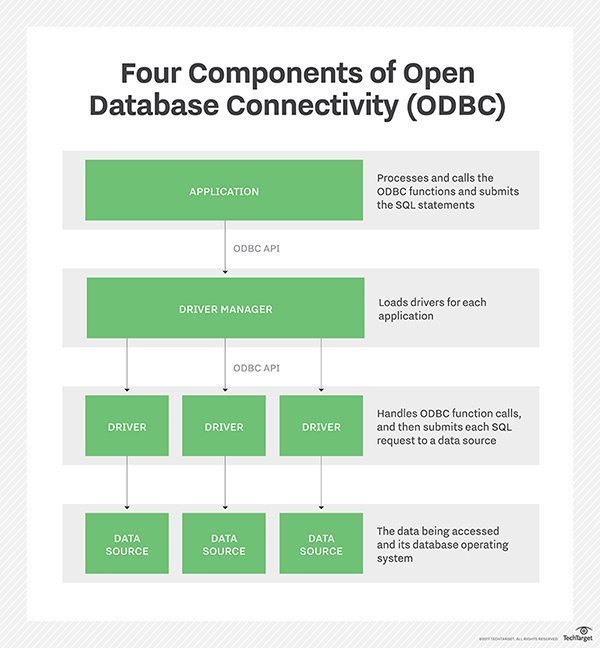
- Application: Processes and calls the ODBC functions and submits the SQL statements;
- Driver manager: Loads drivers for each application;
- Driver: Handles ODBC function calls, and then submits each SQL request to a data source; and
- Data source: The data being accessed and its database management system (DBMS) OS.
OBDC can also work with MySQL when its driver is called MyODBC. Sometimes, this is referred to as the MySQL Connecter/ODBC.
JDBC vs. ODBC
The Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) API uses the Java programming language to access a database. When writing programs in the Java language using JDBC APIs, users can employ software that includes a JDBC-ODBC Bridge to access ODBC-supported databases.
History of Open Database Connectivity
ODBC was created by SQL Access Group and first released in September 1992. Although Microsoft Windows was the first to provide an ODBC product, versions exist for UNIX, OS/2 and Macintosh platforms as well. In June 2016, ODBC said it was developing the newest version, 4.0, but as of September 2017, it had not been released.
In the newer distributed object architecture called Common Object Request Broker Architecture (CORBA), the Persistent Object Service (POS) is a superset of both the CLI and ODBC.
ODBC has remained largely universal since its inception in 1992 and has drivers available for just about all platforms and databases. Thin-client computing, however, has reduced some use of OBDC in the enterprise, as HTML has grown as an intermediate format.