Gateway Definition
A gateway is a network node that connects two networks using different protocols together. While a bridge is used to join two similar types of networks, a gateway is used to join two dissimilar networks.
The most common gateway is a router that connects a home or enterprise network to the internet. In most IP-based networks, the only traffic that doesn’t go through at least one gateway is traffic flowing among nodes on the same local area network (LAN) segment — for example, computers connected to the same switch.
Gateways can take several forms and perform a variety of tasks. These include:
Web application firewall – filters traffic to and from a web server and look at application-layer data.
API, SOA or XML gateway – manages traffic flowing into and out of a service, microservices-oriented architecture or an XML-based web service.
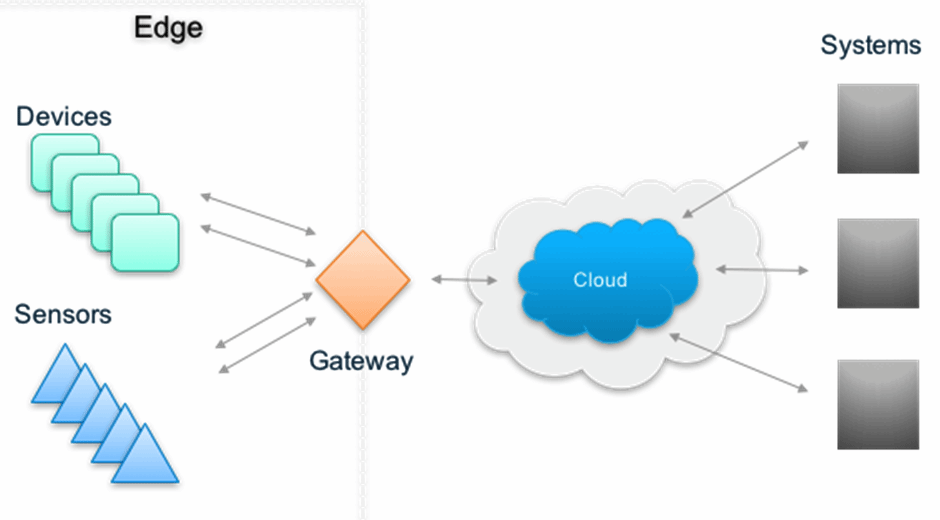
IoT gateway – aggregates sensor data, translates between sensor protocols, processes sensor data before sending it onward and more.
Cloud storage gateway – translates storage requests with various cloud storage service API calls.
Media gateway – converts data from the format required for one type of network to the format required for another.
Amazon API Gateway – allows a developer to connect non-AWS applications to AWS back-end resources.
VoIP trunk gateway – facilitates the use of plain old telephone service (POTS) equipment, such as landline phones and fax machines, with a voice over IP (VoIP) network.
Email security gateway – prevents the transmission of emails that break company policy or will transfer information with malicious intent.