Direct-Attached Storage (DAS)
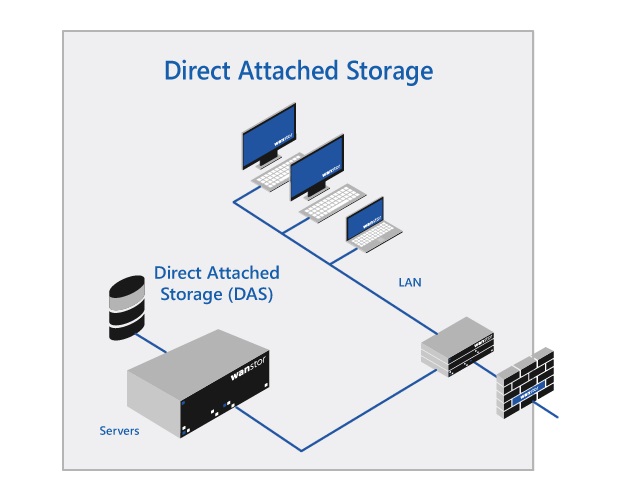
Stands for “Direct Attached Storage.” DAS refers to any storage device connected directly to a computer. Examples include HDDs, SSDs, and optical drives. While DAS can refer to internal storage devices, it is most often describes external devices, such as an external hard drive.
The term “DAS” was created to differentiate between network-attached storage (NAS) and direct-attached storage. Before NAS and storage area networks (SANs) were available, direct-attached storage was the the only option. While DAS is still the most common type of storage used in personal computing, network and server administrators often need to choose between DAS and NAS for a storage solution.
The primary benefit of DAS vs NAS is the simplicity of the setup. You can simply connect a device to a computer and, as long as the necessary drivers are available, it will show up as an additional storage device. There is no need to configure network settings or set up permissions for individual computers. The main drawback of DAS is that a direct-attached device is only accessible via the computer to which it is attached. Therefore, a computer must be configured as a file server in order for other systems to access any connected DAS devices.